Understanding accounts payable definition and process
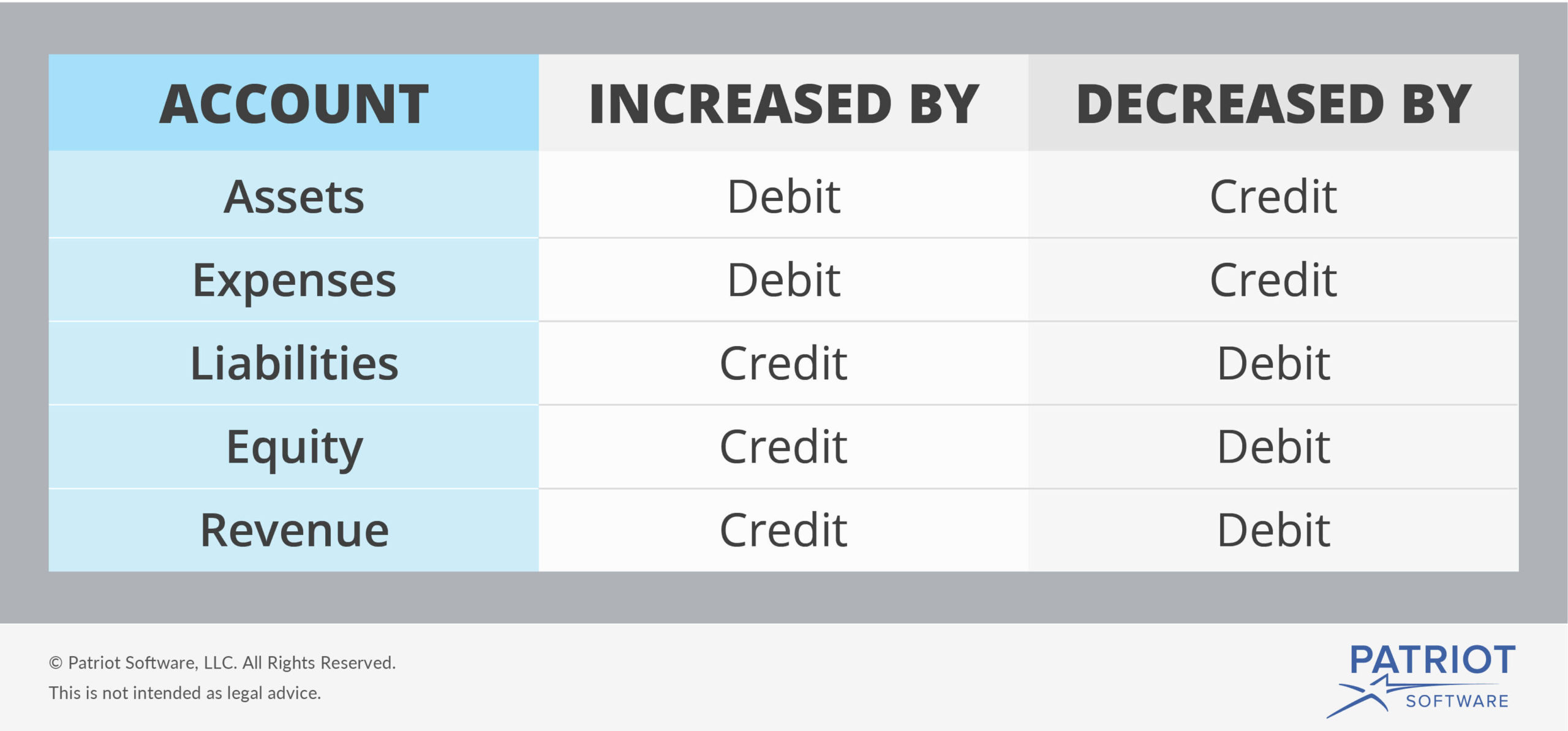
Furthermore, it is recorded as current liabilities on your company’s balance sheet. In general ledger an account titled as “accounts payable account” is maintained to keep record of increases and decrease in accounts payable liability during a period. Since this account is a liability account, its normal balance is credit. When the balance sheet is drawn, the balance shown by this account is reported as current liability.
- To record accounts payable, the accountant credits accounts payable when the bill or invoice is received.
- You can also ensure that you have invoices for all your outstanding purchase orders.
- It records a $500 credit in the accounts payable field and a $500 debit to office supply expense when the AP department receives the invoice.
- Credit your AP account with the amount, and debit the corresponding asset account (like inventory or equipment, depending what you’ve purchased).
- This approach not only aids in maximizing tax deductions, but also in ensuring overall financial and regulatory compliance.
- Your decision to use a debit or credit entry depends on the account you’re posting to and whether the transaction increases or decreases the account.
Accounts payable aging report
Notes payable are a written promise to repay an amount by a specific date. It’s a contract usually from organizations like banks, credit companies, or parent companies. Accounts payable are a type of account that records money you owe to others in the short-term. An accrued expense is an expense your business has incurred but hasn’t yet paid. Expenses that have been accrued will hit your AP account, showing that you have a liability for those accruals. The accruals will be reversed once you make a payment, and your AP account will shrink.
Differences between debit and credit

The ending cash balance in March is the beginning cash balance in April. Review your company’s balance sheet and analyze each asset and liability account to determine the impact on cash flow. Both accounts payable and accounts receivable form an important part of trade credit. It is important for your business to receive trade credit from its suppliers in the form of accounts payable, as it helps finance your production process.
Debits and Credits Example: Loan Repayment
Small expenses such as miscellaneous postage, out-of-pocket office supplies or company meeting lunch are handled as petty cash. AP often handles a supply of sales tax exemption certificates issued to managers to ensure qualifying business purchases don’t include sales tax expenses. Depending on the responsibilities accounts payable receives from a company, they might process requests and distribute funds to cover travel expenses.
Repeat the Process
You would also enter a debit into your equipment account because you’re adding a new projector as an asset. To help you better understand these bookkeeping basics, we’ll cover in-depth explanations of debits and credits and help you online bookkeeping and accounting services learn how to use both. Keep reading through or use the jump-to links below to jump to a section of interest. Here’s a table summarizing the normal balances of the accounting elements, and the actions to increase or decrease them.
An account payable is essentially an extension of credit from the supplier to the manufacturer. It allows the company to generate revenue from supplies or inventory so the supplier can be paid. This includes manufacturers that buy supplies or inventory from suppliers that extend the terms for the payment.
He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University. Once approved the invoice can be entered into the purchase day book or purchase journal. Debits decrease your equity, usually when you pay out dividends, experience losses, or withdraw funds from the business. Both cash and revenue are increased, and revenue is increased with a credit. Expenses are the costs of operations that a business incurs to generate revenues. Chicago Corporation engaged in the following transactions during the month of January.
You as a business can be viewed as a supplier, and your accounts receivables represent the amount of money you lend to your customers. Likewise, you are also a customer of your vendors and your accounts payable represent your borrowings from such suppliers. The transaction would be recorded in your general ledger as a credit to accounts payable, and a debit to the inventory account (an asset account). Then, once you’ve made a payment to the vendor, you would credit the cash account (credit decreases an asset account), and debit your AP account (debt will decrease a liability account). An accounts payable disbursement report is a list of all the entries you’ve created when you process payments to your suppliers. In other words, it shows all payments leaving your AP account over a specified period of time.